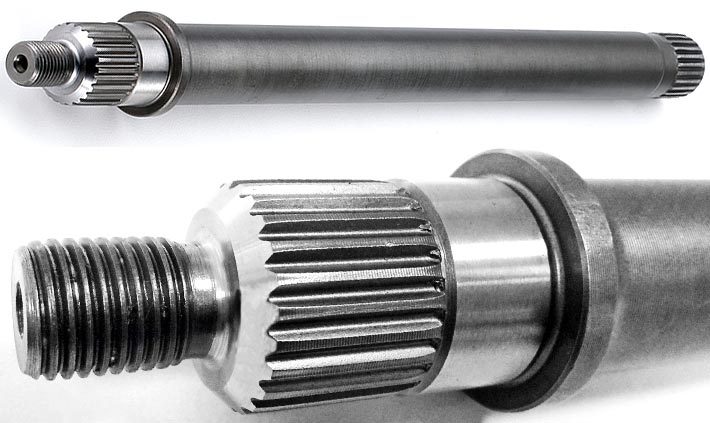
Product Description
Product Description
|
Company Profile
HangZhou Xihu (West Lake) Dis. Machinery Manufacture Co., Ltd., located in HangZhou, “China’s ancient copper capital”, is a “national high-tech enterprise”. At the beginning of its establishment, the company adhering to the “to provide clients with high quality products, to provide timely service” concept, adhere to the “everything for the customer, make customer excellent supplier” for the mission.
Certifications
Q: Where is your company located ?
A: HangZhou ZheJiang .
Q: How could l get a sample?
A: Before we received the first order, please afford the sample cost and express fee. we will return the sample cost back
to you within your first order.
Q: Sample time?
A: Existing items: within 20-60 days.
Q: Whether you could make our brand on your products?
A: Yes. We can print your Logo on both the products and the packages if you can meet our MOQ.
Q: How to guarantee the quality of your products?
A: 1) stict detection during production. 2) Strict completely inspecion on products before shipment and intact product
packaging ensured.
Q: lf my drawings are safe?
A: Yes ,we can CHINAMFG NDA.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | OEM/ODM/Customized |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | OEM/ODM/Customized |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do spline shafts handle variations in torque and rotational force?
Spline shafts are designed to handle variations in torque and rotational force in mechanical systems. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Interlocking Splines:
Spline shafts have a series of interlocking splines along their length. These splines engage with corresponding splines on the mating component, such as gears or couplings. The interlocking design ensures a secure and robust connection, capable of transmitting torque and rotational force.
2. Load Distribution:
When torque is applied to a spline shaft, the load is distributed across the entire engagement surface of the splines. This helps to minimize stress concentrations and prevents localized wear or failure. The load distribution capability of spline shafts allows them to handle variations in torque and rotational force effectively.
3. Material Selection:
Spline shafts are typically made from materials with high strength and durability, such as alloy steels. The material selection is crucial in handling variations in torque and rotational force. It ensures that the spline shaft can withstand the applied loads without deformation or failure.
4. Spline Profile:
The design of the spline profile also contributes to the handling of torque variations. The spline profile determines the contact area and the distribution of forces along the splines. By optimizing the spline profile, manufacturers can enhance the load-carrying capacity and improve the ability of the spline shaft to handle variations in torque.
5. Surface Finish and Lubrication:
Proper surface finish and lubrication play a crucial role in the performance of spline shafts. A smooth surface finish reduces friction and wear, while suitable lubrication minimizes heat generation and ensures smooth operation. These factors help in handling variations in torque and rotational force by reducing the impact of friction and wear on the spline engagement.
6. Design Considerations:
Engineers take several design considerations into account to ensure spline shafts can handle variations in torque and rotational force. These considerations include appropriate spline dimensions, tooth profile geometry, spline fit tolerance, and the selection of mating components. By carefully designing the spline shaft and its mating components, engineers can optimize the system’s performance and reliability.
7. Overload Protection:
In some applications, spline shafts may be equipped with overload protection mechanisms. These mechanisms, such as shear pins or torque limiters, are designed to disconnect the drive temporarily or slip when the torque exceeds a certain threshold. This protects the spline shaft and other components from damage due to excessive torque.
Overall, spline shafts handle variations in torque and rotational force through their interlocking splines, load distribution capability, appropriate material selection, optimized spline profiles, surface finish, lubrication, design considerations, and, in some cases, overload protection mechanisms. These features ensure efficient torque transmission and enable spline shafts to withstand the demands of various mechanical systems.
Can spline shafts be used in automotive applications, and if so, how?
Yes, spline shafts are extensively used in automotive applications due to their ability to transmit torque and provide reliable power transmission. Here’s how spline shafts are used in automotive applications:
Spline shafts play a crucial role in various automotive systems and components, including:
- Drivetrain: Spline shafts are an integral part of the drivetrain system in vehicles. They transmit torque from the engine to the wheels, allowing the vehicle to move. Spline shafts are present in components such as the transmission, differential, and axle shafts. In manual transmissions, the spline shaft connects the transmission input shaft to the clutch disc, enabling power transfer from the engine. In automatic transmissions, spline shafts are used in the torque converter and the output shaft.
- Steering System: Spline shafts are employed in the steering system to transmit torque from the steering wheel to the steering rack or gearbox. They provide a direct connection between the driver’s input and the movement of the wheels, allowing for steering control.
- Power Take-Off (PTO) Systems: Some vehicles, particularly commercial trucks and agricultural machinery, utilize PTO systems. Spline shafts are used in PTOs to transfer power from the vehicle’s engine to auxiliary equipment, such as hydraulic pumps, generators, or agricultural implements.
- Transfer Cases: In four-wheel-drive (4WD) or all-wheel-drive (AWD) vehicles, transfer cases are used to distribute power to the front and rear axles. Spline shafts are utilized in the transfer case to transfer torque between the transmission and the front and rear drive shafts.
- Propeller Shafts: Spline shafts are present in propeller shafts, which transmit torque from the transmission or transfer case to the rear axle in rear-wheel-drive vehicles. They accommodate the relative movement between the transmission and the axle due to suspension travel.
In automotive applications, spline shafts are designed to withstand high torque loads, provide precise torque transmission, and accommodate misalignments and fluctuations in operating conditions. They are typically made from high-strength steel or alloy materials to ensure durability and resistance to wear. Proper lubrication is essential to minimize friction and ensure smooth operation.
The use of spline shafts in automotive applications allows for efficient power transmission, precise control, and reliable performance, contributing to the overall functionality and drivability of vehicles.

How does a spline shaft differ from other types of shafts?
A spline shaft differs from other types of shafts in several ways. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Spline Structure:
A spline shaft features a series of ridges or teeth (splines) that are machined onto its surface. These splines create a precise and controlled interface with mating components, allowing for torque transmission and relative movement. In contrast, other types of shafts, such as plain shafts or keyed shafts, do not have the splines and rely on different mechanisms for torque transmission.
2. Torque Transmission and Relative Movement:
Unlike plain shafts or keyed shafts, which transmit torque through a frictional or mechanical connection, spline shafts allow for both torque transmission and relative movement between the shaft and mating components. The splines on the shaft engage with corresponding splines on the mating component, creating an interlock that transfers rotational force while accommodating axial or radial displacement. This feature provides flexibility and is particularly useful in applications where misalignment or relative movement needs to be accommodated.
3. Load Distribution:
One of the advantages of spline shafts is their ability to distribute loads over a larger surface area. The multiple contact points created by the splines help distribute the applied load evenly along the shaft’s length. This load distribution minimizes stress concentrations and reduces the risk of premature wear or failure. In contrast, other types of shafts may rely on a single keyway or frictional contact, which can result in higher stress concentrations and limited load distribution.
4. Design Flexibility:
Spline shafts offer greater design flexibility compared to other types of shafts. The number, size, and shape of the splines can be customized to meet specific design requirements. This allows for optimization of torque transmission, load-bearing capacity, and relative movement characteristics based on the application’s needs. Other types of shafts may have more standardized designs and limited customization options.
5. Application Variability:
Spline shafts find widespread use in various industries and applications where torque transmission, relative movement, and load distribution are crucial. They are commonly employed in gearboxes, power transmission systems, steering mechanisms, and other rotational systems. Other types of shafts, such as plain shafts or keyed shafts, may be more suitable for applications that require simpler torque transmission without the need for relative movement.
6. Installation and Maintenance:
When compared to other types of shafts, spline shafts may require more precise machining and alignment during installation. The mating components must be accurately matched to ensure proper engagement and torque transfer. Additionally, spline shafts may require periodic inspection and maintenance to ensure the integrity of the splines and optimal performance.
In summary, spline shafts differ from other types of shafts due to their spline structure, ability to accommodate relative movement, load distribution capability, design flexibility, application variability, and specific installation and maintenance requirements. These characteristics make spline shafts well-suited for applications that demand precise torque transmission, flexibility, and load distribution.


editor by CX 2024-05-07